Expansion Cards

PCI slots
What are expansion cards?
Expansion cards are additional components that you plug into the motherboard’s expansion slots to add or enhance features.
The slots are called PCI (on older computers) or PCIe (on newer models).
Common types are graphics cards (video), sound cards (audio), network cards (internet) and capture cards (streaming).



Graphics Card
A graphics card processes images, videos and 3D graphics so they look smooth and realistic. It is used for gaming, video editing, 3D modelling and Virtual Reality (VR).
It has its own processor - the Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) - and dedicated memory (VRAM), so it doesn’t overload the CPU or RAM.
Modern graphics cards can also handle tasks like artificial intelligence (AI) and bitcoin mining.




Graphics cards usually have a cooling system, like a fan, so it doesn't overheat.
The graphics processing unit (GPU) is a chip that renders images and video.
The graphics card has ports such as HDMI or DisplayPort to connect monitors or TVs.
The PCIe connector allows the graphics card to slot onto the motherboard.
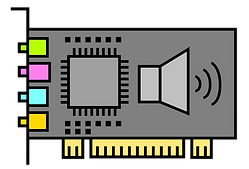
Sound Card
The DAC (Digital-to-Analogue Converter) converts digital data (1s and 0s) from the computer into analogue sound waves for speakers/headphones.
The ADC (Analogue-to-Digital Converter) converts analogue input (like voice from a microphone) into digital data the computer understands.
Jacks are small round sockets where you plug in audio devices like headphones, microphones, or speakers.
The PCIe connector allows the sound card to slot onto the motherboard.
A sound card improves the quality of audio input/output compared to the motherboard’s built-in sound.
They are not needed by most users, because of the motherboard's built-in sound, but they are used by music production, gaming or professional audio work.
It can support surround sound systems, high-quality microphones, and musical instruments using jacks (audio ports).



Integrated cards

-
Built directly into the motherboard.
-
Cheaper, uses less power and is good enough for basic tasks (e.g. web browsing, watching videos and office work).
-
Shares the computer’s RAM and processor (CPU) instead of having its own.
-
An example is integrated graphics on a laptop for browsing and schoolwork.
Dedicated cards
-
These are separate expansion cards (e.g. graphics card or sound card) to connect to the motherboard's PCIe slots.
-
They usually have their own processor and memory (e.g. GPU & VRAM for graphics).
-
Much more powerful, ideal for gaming, video editing, 3D design or professional audio.
-
Uses more power and costs more.