3.1 - Server Types
Exam Board:
OCR
Specification:
2016 - Unit 1
What is a server?
A server is a powerful dedicated system on a network. It requires increased memory, storage and processing power than traditional computer systems to fulfill its role across the network.
Servers need to be scalable - this means they must be adaptable and able to efficiently manage the needs of connected systems if more are added or some are removed.
Servers have different roles so a company may use multiple, separate server types within their organisation, each with a specific purpose. Having separate servers is costly but beneficial as if one loses connection, others may still be usable. Also a server will be more efficient if it is only managing one resource (e.g. printers) at a time.

File Server
A file server centrally stores and manages files so that other systems on the network can access them.
The server provides access security, ensuring that only users of the appropriate access level can access files.
File servers can be used to automatically backup files, as per the organisation's disaster recovery policy.
Using a file server frees up physical storage space within a business and can provide printing services too.
Printer Server
These servers control any printers on a network and manage printing requests by sending the document to an appropriate printer.
Print servers use spooling to queue print jobs so that they are printed when the printer is ready.
If a fault occurs with a certain printer, work can be automatically diverted to another available printer.


Application Server
These servers allow users to access shared applications on a network.
All users will be able to access common applications like email software or word processing, but the server will also restrict certain applications to those with invalid access levels (such as hiding financial databases from employees outside of the finance department).
Application updates can be simply deployed to the application server only, avoiding individual updates for each system and saving a lot of time.
Installers can be hosted on an application server, allowing the software to be easily installed on other connected machines.
Database Server
These servers manage database software that users on the network can access and use to manipulate data.
Data held on the server will be stored in a database accessible from multiple connected computers.
The data can be modified using query languages such as SQL.
Storing data on a database server, rather than individual computers, is more reliable. A database server for a business also allows for scaling - for example, the database can be increased in size if the customer base grows.

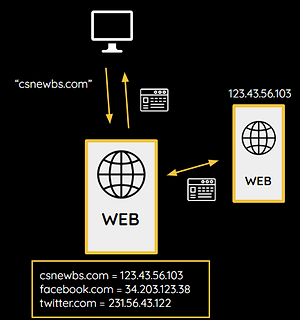
Web Server
A web server manages HTTP requests from connected devices to display web pages on web browsers.
A request (e.g. csnewbs.com) is sent to the web server.
The server contains a list of known URLs and their matching IP addresses.
The server contacts the server where the web page is held and delivers the web page to the client.
Mail Server
These servers send and receive emails using email protocols (SMTP & POP) allowing email communication between other mail servers on other networks.
The server makes sure emails are delivered to the correct user on the network.
Email servers can store company address books making internal communication easier for organisations.
The server may have anti-spam functions to reduce junk mail.

Hypervisor

A hypervisor allows a host machine to operate virtual machines as guest systems. The virtual machines share the resources of the host, including its memory, processing power and storage space.
This type of technology is called virtualisation. The guest machines are isolated so if one failed, the other guests and the hosts are not affected - demonstrating good security.
The hypervisor optimises the hardware of the host server to allow the virtual machines to run as efficiently as possible.
Questo's Questions
3.1 - Server Types:
1a. What is a server? Why does it need to be scalable? [2]
1b. Give two reasons why a company may use multiple, separate servers. [2]
1c. State the 7 types of server. [1 each]
2. A medium-sized animation company working on a movie are considering buying a server. Describe each type of server and the different roles they have.
a. File Server
b. Printer Server
c. Application Server
d. Database Server
e. Web Server
f. Mail Server
g. Hypervisor [4 each]
3. What type of technology does a hypervisor use to control multiple virtual machines? [1]